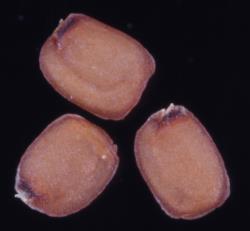
Perennial herb, single rosette or with short lateral branches, stem and branches up to 3 mm diam. Leaves up to 50 mm long, usually glabrous or rarely the lamina and petiole margins sparsely hairy; lamina 5.0–20.0 × 2.0–9.5 mm, green, purple-brown, brown-green or bronze, coriaceous, glossy, obovate, broadly obovate, obovate-orbicular, or oblong-elliptic, simple or pinnatifid; apex obtuse, usually with a distinct hydathode; base cuneate to attenuate, grading into petiole.. Lateral lobes 1–4, basal, 1.3–3.0 × 1.0–1.7 mm, rarely with 1–4 teeth near apex. Petiole up to 35 mm long, plano-convex. Cauline leaves absent. Inflorescence usually racemose with 5–11 flowers, sometimes in loose whorls or almost corymbose; peduncle up to 110 mm long, 0.5–1.0 mm diam. at base, ascending to erect, glossy, glabrous, green to brown-green. Pedicels up to 30 mm long, 0.3–0.4 mm diam., terete, flexuose. Sepals 2.0–2.5 × 0.8–1.1 mm, oblong, ± saccate, purple-green or purple, glabrous or rarely sparsely hairy, margin white and membranous, apex obtuse, base truncate. Petals 4.0–7.0 × 1.0–2.5 mm, white, limb obovate; apex obtuse; base attenuate, tapering into the ± indistinct claw. Stamens 6; median filaments 4, 2.6–4.0 mm long; lateral filaments 2, 2.2–3.3 mm long; anthers 0.4–0.5 mm long, yellow or maroon, held at a similar height to or overtopping the stigma. Ovary 2.4–3.8 mm long, 0.4–0.7 mm diam., ± terete, green, glabrous; ovules 22–28; style 0.2–0.9 mm long, ± terete; stigma 0.2–0.4 mm diam. Siliques 17–32 × 1.1–1.2 mm, erect, glabrous, valves purple-brown to green at maturity, style 0.3–0.5 mm long. Seeds 0.9–1.3 mm long, 0.55–0.95 mm wide, 0.2–0.3 mm thick, broadly oblong, henna to pale yellow; wing absent or rarely present but very narrow.
Cardamine dimidia is distinguished from C. bilobata by its more compact growth habit, shorter inflorescences, smaller sepals and petals, slightly shorter filaments, and usually longer silique with a short style.
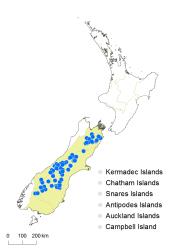
South Island: Sounds Nelson, Marlborough, Westland, Canterbury, Otago, Southland.
Cardamine dimidia is a South Island endemic, being primarily confined to the Southern Alps and adjacent eastern South Island mountains.
Cardamine dimidia primarily occurs on bluffs and rock outcrops, where it usually grows in shaded crevices and on ledges, and it also occurs in sheltered sites among large boulders.
Cardamine dimidia is assessed as having a conservation status of Not Threatened (de Lange et al. 2018).
Putative hybrids possibly involving C. dimidia have been collected in the field (Heenan 2017). These include C. dimidia × C. glara (CHR 514766, Yeo Stream, Marlborough; CHR 629749, Castle Hill Basin, Canterbury) and C. dimidia × C. eminentia (CHR 517634; Livingston Mountains, Southland).
Flowering September–April; Fruiting December–April.
There is some regional variation in leaf shape. Populations from the vicinity of Mt Cook (South Canterbury) are characterised by plants with leaves broader and more rounded in shape, being obovate-orbicular. Collections from Torlesse Range, Craigieburn Mountains and Puketeraki Range have distinctly pinnatifid to pinnatisect leaves.